大多数语言模型都有一个共同点:对于通过互联网传输的资源来说,它们都相当大。最小的 MediaPipe 对象检测模型 (SSD MobileNetV2 float16) 大小为 5.6 MB,最大的约为 25 MB。
开源大语言模型 (LLM) gemma-2b-it-gpu-int4.bin 的大小为 1.35 GB,对于 LLM 而言,这被认为是极小的。
生成式 AI 模型可能非常庞大。因此,如今许多 AI 用例都在云端实现。越来越多的应用直接在设备上运行高度优化的模型。虽然目前已有在浏览器中运行 LLM 的演示,但下面是一些在浏览器中运行的其他模型的生产级示例:
- Adobe Photoshop 在设备端运行
Conv2D模型的变体,以实现智能对象选择工具。 - Google Meet 运行经过优化的
MobileNetV3-small模型,以实现人员分割,从而实现背景模糊功能。 - Tokopedia 运行
MediaPipeFaceDetector-TFJS模型,以进行实时人脸检测,防止用户无效注册其服务。 - Google Colab 允许用户在 Colab 笔记本中使用硬盘中的模型。
为了加快应用未来的启动速度,您应该在设备上显式缓存模型数据,而不是依赖隐式的 HTTP 浏览器缓存。
虽然本指南使用 gemma-2b-it-gpu-int4.bin 模型来创建聊天机器人,但该方法可以进行泛化,以适应其他模型和设备上的其他使用情形。将应用连接到模型的最常见方法是,将模型与应用的其余资源一起提供。优化投放至关重要。
配置正确的缓存标头
如果您从服务器提供 AI 模型,请务必配置正确的 Cache-Control 标头。以下示例展示了一个可靠的默认设置,您可以根据应用的需求在此基础上进行调整。
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000, immutable
AI 模型的每个已发布版本都是静态资源。对于永不更改的内容,应为其设置较长的 max-age,并在请求网址中结合使用缓存失效。如果您确实需要更新模型,则必须为其提供新网址。
当用户重新加载网页时,即使服务器知道内容是稳定的,客户端也会发送重新验证请求。immutable 指令明确表示无需重新验证,因为内容不会更改。浏览器和中间缓存或代理服务器并不广泛支持 immutable 指令,但通过将其与普遍理解的 max-age 指令结合使用,您可以确保最大限度的兼容性。public 响应指令表示响应可以存储在共享缓存中。
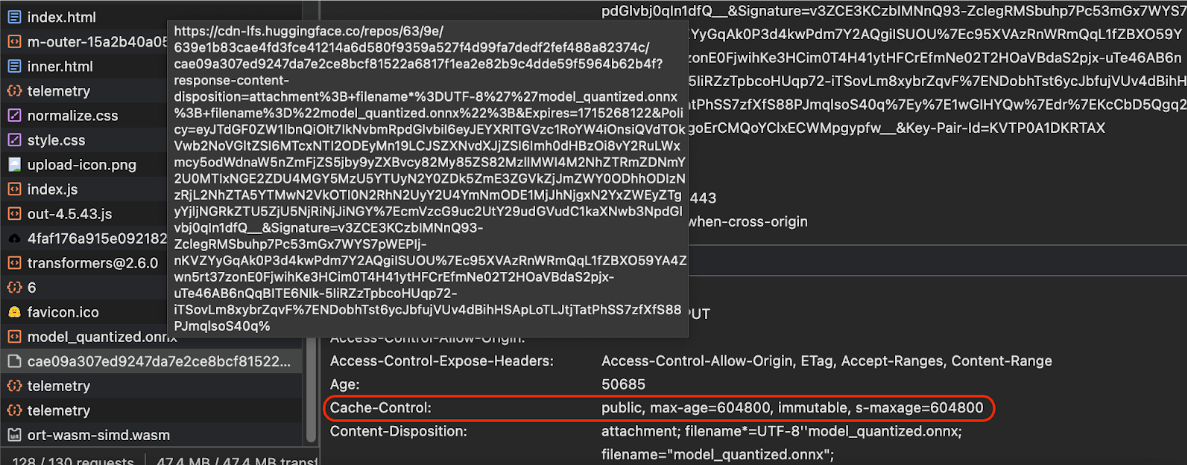
Cache-Control 标头。
(来源)
在客户端缓存 AI 模型
部署 AI 模型时,请务必在浏览器中显式缓存该模型。这样可确保在用户重新加载应用后,模型数据可随时使用。
您可以使用多种技巧来实现这一目标。对于以下代码示例,假设每个模型文件都存储在内存中名为 blob 的 Blob 对象中。
为了解性能,每个代码示例都使用 performance.mark() 和 performance.measure() 方法进行了注释。这些指标取决于设备,无法进行泛化。
您可以选择使用以下 API 之一在浏览器中缓存 AI 模型:Cache API、Origin Private File System API 和 IndexedDB API。一般建议是使用 Cache API,但本指南会讨论所有选项的优缺点。
Cache API
Cache API 为缓存到长期内存中的 Request 和 Response 对象对提供持久性存储。虽然该 API 在 Service Workers 规范中定义,但您可以在主线程或常规 worker 中使用它。如需在服务工作线程上下文之外使用它,请使用合成 Response 对象(而非 Request 对象)调用 Cache.put() 方法,并搭配使用合成网址。
本指南假定您使用的是内存中的 blob。使用虚假网址作为缓存键,并使用基于 blob 的合成 Response。如果您要直接下载模型,可以使用通过发出 fetch() 请求获得的 Response。
例如,以下代码展示了如何使用 Cache API 存储和恢复模型文件。
const storeFileInSWCache = async (blob) => {
try {
performance.mark('start-sw-cache-cache');
const modelCache = await caches.open('models');
await modelCache.put('model.bin', new Response(blob));
performance.mark('end-sw-cache-cache');
const mark = performance.measure(
'sw-cache-cache',
'start-sw-cache-cache',
'end-sw-cache-cache'
);
console.log('Model file cached in sw-cache.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
};
const restoreFileFromSWCache = async () => {
try {
performance.mark('start-sw-cache-restore');
const modelCache = await caches.open('models');
const response = await modelCache.match('model.bin');
if (!response) {
throw new Error(`File model.bin not found in sw-cache.`);
}
const file = await response.blob();
performance.mark('end-sw-cache-restore');
const mark = performance.measure(
'sw-cache-restore',
'start-sw-cache-restore',
'end-sw-cache-restore'
);
console.log(mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
console.log('Cached model file found in sw-cache.');
return file;
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
};
Origin Private File System API
源专用文件系统 (OPFS) 是一种相对较新的存储端点标准。它对网页来源是私有的,因此与常规文件系统不同,用户无法看到它。它提供对特殊文件的访问权限,该文件经过高度优化以实现高性能,并提供对其内容的写入访问权限。
例如,以下代码展示了如何在 OPFS 中存储和恢复模型文件。
const storeFileInOPFS = async (blob) => {
try {
performance.mark('start-opfs-cache');
const root = await navigator.storage.getDirectory();
const handle = await root.getFileHandle('model.bin', { create: true });
const writable = await handle.createWritable();
await blob.stream().pipeTo(writable);
performance.mark('end-opfs-cache');
const mark = performance.measure(
'opfs-cache',
'start-opfs-cache',
'end-opfs-cache'
);
console.log('Model file cached in OPFS.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
};
const restoreFileFromOPFS = async () => {
try {
performance.mark('start-opfs-restore');
const root = await navigator.storage.getDirectory();
const handle = await root.getFileHandle('model.bin');
const file = await handle.getFile();
performance.mark('end-opfs-restore');
const mark = performance.measure(
'opfs-restore',
'start-opfs-restore',
'end-opfs-restore'
);
console.log('Cached model file found in OPFS.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
return file;
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
};
IndexedDB API
IndexedDB 是一种成熟的标准,用于在浏览器中以持久方式存储任意数据。IndexedDB 以其略显复杂的 API 而闻名,但通过使用封装容器库(例如 idb-keyval),您可以将 IndexedDB 视为经典键值存储区。
例如:
import { get, set } from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/idb-keyval@latest/+esm';
const storeFileInIDB = async (blob) => {
try {
performance.mark('start-idb-cache');
await set('model.bin', blob);
performance.mark('end-idb-cache');
const mark = performance.measure(
'idb-cache',
'start-idb-cache',
'end-idb-cache'
);
console.log('Model file cached in IDB.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
};
const restoreFileFromIDB = async () => {
try {
performance.mark('start-idb-restore');
const file = await get('model.bin');
if (!file) {
throw new Error('File model.bin not found in IDB.');
}
performance.mark('end-idb-restore');
const mark = performance.measure(
'idb-restore',
'start-idb-restore',
'end-idb-restore'
);
console.log('Cached model file found in IDB.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
return file;
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
};
将存储标记为持久
在上述任何一种缓存方法的末尾调用 navigator.storage.persist(),以请求使用持久性存储空间的权限。如果已授予权限,此方法会返回一个解析为 true 的 promise;否则,会返回一个解析为 false 的 promise。浏览器可能会或可能不会遵循该请求,具体取决于浏览器特定的规则。
if ('storage' in navigator && 'persist' in navigator.storage) {
try {
const persistent = await navigator.storage.persist();
if (persistent) {
console.log("Storage will not be cleared except by explicit user action.");
return;
}
console.log("Storage may be cleared under storage pressure.");
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
}
特殊情况:使用硬盘上的模型
您可以直接从用户的硬盘引用 AI 模型,而不是使用浏览器存储空间。此技术可帮助研究型应用展示在浏览器中运行给定模型的可行性,或允许艺术家在专业创意应用中使用自行训练的模型。
File System Access API
借助 File System Access API,您可以打开硬盘中的文件并获取可持久保存到 IndexedDB 的 FileSystemFileHandle。
采用此模式,用户只需授予一次模型文件访问权限。借助持久权限,用户可以选择永久授予对文件的访问权限。重新加载应用并执行所需的用户手势(例如点击鼠标)后,可以从 IndexedDB 恢复 FileSystemFileHandle,并访问硬盘上的文件。
系统会查询文件访问权限,并在必要时请求这些权限,从而确保未来重新加载时不会出现问题。以下示例展示了如何从硬盘获取文件句柄,然后存储和恢复该句柄。
import { fileOpen } from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/browser-fs-access@latest/dist/index.modern.js';
import { get, set } from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/idb-keyval@latest/+esm';
button.addEventListener('click', async () => {
try {
const file = await fileOpen({
extensions: ['.bin'],
mimeTypes: ['application/octet-stream'],
description: 'AI model files',
});
if (file.handle) {
// It's an asynchronous method, but no need to await it.
storeFileHandleInIDB(file.handle);
}
return file;
} catch (err) {
if (err.name !== 'AbortError') {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
}
});
const storeFileHandleInIDB = async (handle) => {
try {
performance.mark('start-file-handle-cache');
await set('model.bin.handle', handle);
performance.mark('end-file-handle-cache');
const mark = performance.measure(
'file-handle-cache',
'start-file-handle-cache',
'end-file-handle-cache'
);
console.log('Model file handle cached in IDB.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.name, err.message);
}
};
const restoreFileFromFileHandle = async () => {
try {
performance.mark('start-file-handle-restore');
const handle = await get('model.bin.handle');
if (!handle) {
throw new Error('File handle model.bin.handle not found in IDB.');
}
if ((await handle.queryPermission()) !== 'granted') {
const decision = await handle.requestPermission();
if (decision === 'denied' || decision === 'prompt') {
throw new Error('Access to file model.bin.handle not granted.');
}
}
const file = await handle.getFile();
performance.mark('end-file-handle-restore');
const mark = performance.measure(
'file-handle-restore',
'start-file-handle-restore',
'end-file-handle-restore'
);
console.log('Cached model file handle found in IDB.', mark.name, mark.duration.toFixed(2));
return file;
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
};
这些方法并不相互排斥。在某些情况下,您可能既需要在浏览器中显式缓存模型,又需要使用用户硬盘中的模型。
演示
您可以在 MediaPipe LLM 演示中看到实现的所有三种常规情形存储方法和硬盘方法。
奖励:以分块形式下载大型文件
如果您需要从互联网下载大型 AI 模型,请将下载并行化为单独的块,然后在客户端上重新拼接。
软件包 fetch-in-chunks 提供了一个可在代码中使用的辅助函数。您只需向其传递 url。maxParallelRequests(默认值:6)、chunkSize(默认值:要下载的文件大小除以 maxParallelRequests)、progressCallback 函数(用于报告 downloadedBytes 和总 fileSize)以及 AbortSignal 信号的 signal 都是可选的。
import fetchInChunks from 'fetch-in-chunks';
async function downloadFileWithProgress() {
try {
const blob = await fetchInChunks('https://example.com/largefile.zip', {
progressCallback: (downloaded, total) => {
console.log(`Downloaded ${((downloaded / total) * 100).toFixed(2)}%`);
},
});
return blob;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching file:', error);
}
}
downloadFileWithProgress();
选择适合您的方法
本指南探讨了在浏览器中有效缓存 AI 模型的各种方法,这项任务对于提升用户体验和应用性能至关重要。Chrome 存储团队建议使用 Cache API 来获得最佳性能,确保快速访问 AI 模型,缩短加载时间并提高响应速度。
OPFS 和 IndexedDB 是不太实用的选项。OPFS 和 IndexedDB API 需要先序列化数据,然后才能存储数据。IndexedDB 在检索数据时还需要对数据进行反序列化,因此它是存储大型模型的糟糕选择。
对于小众应用,File System Access API 可直接访问用户设备上的文件,非常适合管理自有 AI 模型的用户。
如果您需要保护 AI 模型,请将其保留在服务器上。一旦存储在客户端上,便可使用开发者工具或 OFPS 开发者工具扩展程序轻松从缓存和 IndexedDB 中提取数据。 这些存储 API 在安全性方面本质上是相同的。您可能想存储模型的加密版本,但这样一来,您就需要将解密密钥提供给客户端,而这可能会被拦截。这意味着,恶意行为者窃取您的模型的难度会略有增加,但并非不可能。
我们建议您选择与应用的要求、目标受众群体行为和所用 AI 模型的特征相符的缓存策略。这可确保您的应用在各种网络条件和系统限制下都能保持响应性和稳健性。
致谢
此文档由以下人员审核:Joshua Bell、Reilly Grant、Evan Stade、Nathan Memmott、Austin Sullivan、Etienne Noël、André Bandarra、Alexandra Klepper、François Beaufort、Paul Kinlan 和 Rachel Andrew。

